Water Quality

To better manage water resources in the Chehalis Basin, it is important to understand the water quality in the Chehalis River and its tributaries. Water quality studies in the Chehalis Basin (links below) have shown that many parts of the Chehalis River have high temperatures and low oxygen in the summer. Both of these conditions are harmful to aquatic life living in the river and its tributaries. Today, the Chehalis Tribe is monitoring water quality in some streams and the mainstem Chehalis River using “grab samples.” The Department of Ecology currently maintains continuous water quality measurement equipment in some locations in the upper watershed (links below).
The Partnership’s goal for water quality is to prevent degradation and improve water quality so as to have clean water for all fish, wildlife, and human uses. It will take the combined effort of people living in the whole watershed to keep the water clean.
State of the Watershed: Water Quality
Site has data on current and historic water quality for a variety of locations throughout the Chehalis
This report provides information on a water quality study based on samples taken at 94 sites around the Chehalis Basin.
State of the River 2006-2007 (2007)
This is a preliminary assessment based on one year of water quality monitoring.
Total Maximum Daily Load
Chehalis Basin TMDL Update Memo (2021). January, 2021. Provides an update on the status of addressing TMDLs through voluntary actions and related programs in the Chehalis Basin.
Department of Ecology’s Total Maximum Daily Load webpage for the Chehalis Basin. This website describes TMDL plans that cover all of the upper watershed in WRIA 23 and address 303(d) listings for dissolved oxygen (DO), fecal coliform bacteria, and temperature (T) impairments. The site describes current water quality issues, clean-up plans, and actions being taken to fix those problems.
TMDL Implementation Plan (2004): The Chehalis/Grays Harbor Watershed Dissolved Oxygen, Temperature, and Fecal Coliform Bacteria TMDL: Detailed Implementation (Cleanup) Plan.
TMDL Effectiveness Review (2010): Upper Chehalis River Watershed Multi-Parameter Total Maximum Daily Load: Water Quality Data Review (Fecal Coliform)
Other Water Quality Reports
Water Quality Progress Review (2007-2008)
Fecal Coliform Monitoring in Grays Harbor County (2000-2003)
Chehalis Watershed Monitoring Plan
Chehalis River Watershed EPA Success Study
Evaluating Standards for Protecting Aquatic Life in Washington’s Surface Water Quality Standards: Temperature Criteria – Draft Discussion Paper and Literature Summary. Washington State Department of Ecology, 2002. https://apps.ecology.wa.gov/publications/documents/0010070.pdf
What You Can Do to Help Keep Water Clean in the Chehalis
For municipalities: Stormwater treatment funding opportunities: Sign up for the Department of Ecology’s stormwater funding listserve
For landowners: How to get involved in a stream restoration project.
Here is information about how hot water impacts salmon, and what you can do to help.
Have you seen something that you think might be polluting water? You can place a confidential report to the Department of Ecology via: 360-407-6300. See this website for more details http://www.ecy.wa.gov/reportaproblem.html
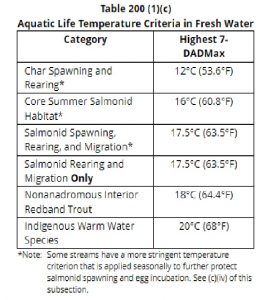
What temperatures do fish need?
Salmon need cool water to migrate, rear and spawn. The following table shows temperature limits by type of fish:
Source: WAC 173-201A-602
Temperature needs vary by season. More information can be found here: https://apps.ecology.wa.gov/publications/documents/0610038.pdf